The problem of unemployment is very serious and it is closely associated with the problem of poverty.
Simply speaking, when all the willing persons in a country do not get work on the current rate of wages it is called unemployment.
Otherwise speaking, if a person, who is able and willing to work, does not get work at the prevailing wage rate, he is called unemployed.
“Problem of unemployment has taken a serious turn and there is apprehension of its becoming still more grim in the future.”-Bhagwati Committee.”
According to Prof. Pigou, “A man is unemployed only when he is both without a job or not employed and also desires to be employed.”
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Classification of Unemployment:
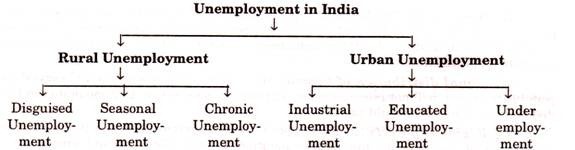
Unemployment in India can be classified into two parts:
(a) Rural unemployment:
Most of the population in India lives in villages. Large number of unemployment is found in villages.
It is of 3 types:
(i) Disguised unemployment:
There is disguised unemployment in rural areas. It is a situation in which more persons are employed to do a job which can be done with equal efficiency by less number of labour forces.
(ii) Seasonal unemployment:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Agriculture is the main source of unemployment in rural areas. Agriculture is a seasonal profession. The agriculture workers remain free during most of the months in a year.
(iii) Chronic unemployment:
Employment opportunities in villages and agriculture remain limited and working force keeps on growing fast. Hence there is chronic unemployment or normal unemployment among agricultural workers.
(b) Urban unemployment:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Unemployment found in urban areas is called Urban unemployment.
It is of 3 types:
(i) Industrial unemployment:
Due to urbanisation, people from rural areas are migrating to towns. There are more workers than industries. So there is unemployment among industrial workers.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(ii) Educated unemployment:
Unemployment among educated persons is called educated unemployment. It is very much common in India due to faulty education system. Unemployment among educated women is higher than educated man.
(iii) Under employment:
Under employment refers to that situation under which a labour does not get full time job or gets job much below his capacities and qualification.
Otherwise speaking he remains without work for some months in a year or some days in a month or for some hours in a day. If a person does not get work for 273 days in a year or 8 hours per day, he will be called as under employed.
Types of Unemployment:
Unemployment is of following types:
(a) Frictional Unemployment:
Frictional unemployment is the unemployment associated with the changing of jobs in dynamic economy. Due to faults in labour market worker may be unemployed temporarily.
This temporary unemployment is called ‘Frictional Unemployment’.
It occurs due to:
(i) Immobility of labour.
(ii) Shortage of raw-material.
(iii) Lack of information regarding employment opportunities.
(iv) Shortage of power.
(v) Wear and tear of machines.
(vi) Tendency of workers to shift from jobs.
(vii) Search for better jobs.
(b) Structural Unemployment:
According to Gardener, “Structural unemployment is the unemployment that results from the long-term decline of certain industries.”
It occurs due to structural changes in the economy:
(i) When other factors of production like capital, land etc. are in shortage.
(ii) When labourers are trained in old industries.
(iii) When labourers are ill-equipped for new industries.
(iv) When there is a change in production technique.
(c) Technological Unemployment:
Unemployment arising out of rapid technological progress is called technological unemployment e.g. introduction of roller, bulldozer, JCB machines and earth remover in road construction may remove the workers engaged in road construction. This is called technological unemployment. Generally capital intensive technology creates technological unemployment.
(d) Voluntary Unemployment:
It refers to the situation when a person is unemployed because he is not willing to work at the existing wage rate even when work is available e.g. If the market wage rate for college lecturer’s job is Rs. 10,000 p.m. but a college lecturer refuses to accept it. It is called voluntary unemployment.
(e) Involuntary Unemployment:
Involuntary unemployment is a situation in which the jobs are not available in the prevailing wage rate. According to Hanson, “Involuntary unemployment is a situation in which people are able to work and willing to work at existing rate of wages but do not get work.”