Read this article to learn about how location factors plays and important role in the manufacturing industries!
Textile Industry:
The term textile, derived from Latin “texere” (to weave). The manufacture of textile fabrics is the oldest and widespread industry in the world based on cotton and wool.
This was first developed in Britain. These are located mainly in relation to power and labour supplies.
The industry strikes a judicious balance between tradition and modernity, labour saving economy and labour intensive approach. On the one hand we have the hand woven khadi sector and on the other, the most modern capital intensive sector. Today the industry stands next to agriculture in providing employment opportunities.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Certain conditions needed for textile industry.
1. Readily available raw materials (Cotton, Jute, Silk, Wool)
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. Ample supplies of soft, good quality water for processing
3. Power supply and efficient skilled labourers
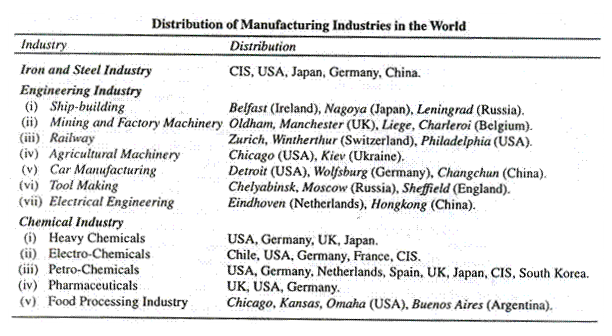
4. Well – developed domestic and external market. Iron and Steel Industry
The manufacture of iron and steel is one of the basic industries because these are used for making machinery which is necessary for all types of Industries. It is a heavy industry and raw materials include iron ore, cooking coal and limestone. This industry calls for continual updating of technology, “R and D” (Research and Development) support and long waiting time before it yields dividends.
The iron and steel plants consists of:
1. Coke ovens for converting coal into coke.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. Blast furnaces to reduce iron ore to pig iron
3. Steel furnaces to make steel from pig iron adding carbon and ferro alloys.
4. Rolling mills for shaping up steel into different forms.
Four factors required for development of an integrated plant.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
1. Abundant supply of iron,
2. Large supply of good heating and coking coal,
3. Nearness to a densely populated region and industrialised market with large demand for iron products,
4. Adequate supply of capital and labour of managerial efficiency.
Sugar Industry:
Sugar Industry is widely scattered and is a rural based industry. This industry started in private sector and was largely confined to Uttar Pradesh and Bihar but now it is widely spread. It is a seasonal industry and so it is better suited to the cooperative sector. India is the largest producer of sugar.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It stands first in world production because of putting sugar Khandsari and Gur or Jaggery together. This industry should be given attention as it earns foreign exchange. We are facing a stiff competition from Cuba and Indonesia in the International market.
Fertilizer Industry:
Fertilizer has become a key input in Indian agriculture, after the Green Revolution. It’s use has increased on a large scale after its adoption as a strategy for agricultural development. The use of fertilizer was almost non-existent. By 1950-51 a modest beginning was made in producing fertilizers at home.
The setting up of Fertilizer Corporation of India (FCI) in 1961 and National Fertilizers Ltd. (NFL) in 1974 provided a sound base to this industry. The manufacturing units produce nitrogenous, complex and phosphatic fertilizers and single, superphosphate. The progress of this industry is evident from its production level like 9 thousand of nitrogenous fertilizers (1950-51) to 72.4 lakh tonnes in 1991-92.
Six Large Sizes Nitrogenous Plants:
1. Bijapur − Madhya Pradesh
2. Sawai Madhopur − Rajasthan
3. Aonla, Dabrala Jagdishpur − Shahjahanpur (U.P.)
4. Kakinada − Andhra Pradesh