Animals are very useful for us as we get food, wool, milk, honey, and we use animals for transportation.
Dr. Verghese Kurien born 26 November, 1921 at Kerala, He is called the ‘father of the white Revolution’ in India.
He was the chairman of the Gujarat Co-operative Marketing Federation. He is credited with being the architect of operation flood the largest dairy development program in the world. He engineered the white Revolution in India, and made India the largest milk producer in the world.
He has done B.E. (Mech) from Madras University and joined Tate Steel at Jamshedpur. He went to USA and earned Master of Science in Mechanical engineering (with distinction) from Michigan State University. When he came back to India, he was posted as a diary engineer at the government creamery, Anand.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Milk producing animals:
Milk producing animals of India are cows, buffaloes, goats and camels. The milk from goat is nutritions and some time preferred to cow milk. But the production of goat milk is comparatively less than that of dairy breeds of cows and buffaloes.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The milk of buffaloes contains more fat than cow’s milk. Buffaloes are the major source of milk in our country. Bullock is an important animal for farmers. It is used for ploughing the fields, transportation and many other agricultural activities. The dung of animals is also very useful in ‘gobar gas’ plants to produce bio-gas. Dung cakes are used as fuel in villages. Hides of these animals is used to manufacture leather, leather is used to make different articles such as shoes, belts, purses, and jackets. Camels are used in camel carts.
Sheep and Goat:
Sheep and goats provide us meat, wool and hide. Sheep (Fig. 12.6) are very common animal found every- where in the world. Sheep are timid and very useful to us. New Zealand, USA, South Africa and Australia are leading sheep producing countries. Sheep feed on grass, herbs, shrubs and grains. Sheep are milk producing animals, give us wool and leather. We use their meat as food.
The process of removal of wool from sheep is called shearing (Fig. 12.7). Wool is produced from the fleece of sheep. Power shears are used for shearing. The quality of wool varies from breed to breed. Pashmina wool is very soft and warm and it is obtained from Indian breed called Pashmina, which is found in Kashmir and Himalayan areas.
Pig:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Rearing of pig is called piggery. Pigs provide us meat which is called pork. The pork should be very well cooked as it acts as the host of tapeworm. Pigs should be provided with good quality of feed.
Poultry:
Rearing of hen, ducks, turkey and doves to get meat and egg is known as poultry (Figs. 12.8-12.10). The domestic birds give us meat and egg. The egg and meat are rich in proteins fat, vitamins and minerals like iron, calcium and phosphate. The oats, peas, grams and beans are good food for fowls. Several breeds of fowls have been developed but broiler is the best for meal. Rock, blackminorca, light brahma and Rhode Island Red are the other varieties of fowl.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Fish:
The production and management of fishes is known as pisciculture. Fish farms are a good resource of animal food. A large section of Indian population use fish as food. Fish is a rich source of protein. Fishes are aquatic animals and their production is also called water-agriculture (Figs. 12.11-12.13). We also get different types of oils from fishes. There are different types of fishes such as Rohu, Singhi and Catla these are found in fresh water, marine water fishes are Sardine, Hilsa and Tuna. Fish keeping fish, liver oil provides us proteins, vitamins A and D.
Honeybee:
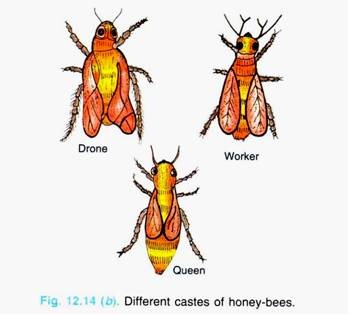
Rearing of honey-bee is called apiculture. Honey-bees (Fig. 12.14a) are highly organised social insects living in colonies. A good and well developed colony of bees has 40 to 50 thousand individuals which has 3 castes i.e., queen, drone and worker (Fig. 12.14b).
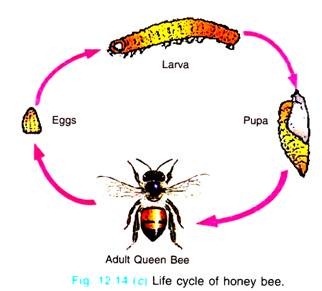
The nest of honey bees is called hive. The hive is divided into many compartments called combs. There is only one queen in honeycomb. She is the supreme being in the colony. The drones are the male members but stouter than the queen with broader abdomen. The function of drones is to fertilize the eggs laid by the queen (Fig. 12.14c).
After fertilization drones are driven out of the hive to die of hunger and heat. The workers are darker and smaller having strongest mouth parts and well developed wings. They have four pairs of pocket-like wax-secreting glands. The particular place of breeding of honeybees to get honey and wax for commercial purpose is known as Apiary. It is the nectar that the bees turn into honey.
Honey is a good source of nutrients. It contains 80% sugar in it. Water, enzymes and other constituents are present in honey. Food value of honey is high. It is estimated that 200 gm of honey provides as much nourishment as 12.5 litre of milk. Honey is used as preservative in the preparation of Ayurvedic and unani medicines. Bee-wax is used in making cosmetics, face- creams, paints, ointments, polishes, carbon paper and other lubricants.
Silk moth:
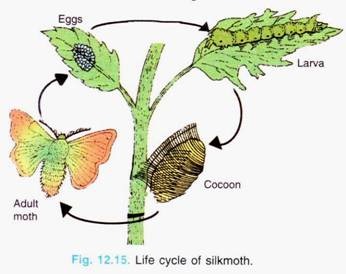
Rearing of silk moth is called sericulture (12.15). The silkworm lives on mulberry plants. The female silk moth lays eggs in clusters upon mulberry leaves. A minute larva hatches out from each egg in about 10 days. The larva voraciously feeds upon mulberry leaves and undergoes four moults. After fourth moult, the larva stops feeding and starts pouring out its sticky saliva. As this saliva comes out in the air, it changes into solid silk-thread. Now the larva wrap itself around the silk-thread forming a cocoon.
The cocoons are put into hot water or subjected to steam or dry heat, this way cocoons are killed. Killing of cocoons is called stifling. This helps in softening the adhesion of the silk thread. Now the thread is removed, this process is called realing and spinning. Now the raw silk is wound around a large wheel.
This raw silk is twisted into the thread of silk. Raw silk is used to make woven materials and knitted fabrics. Parachutes, parachute cords and fishing rods are made by silk. Insulation cords for telephone and wireless receivers are made by silk. Mysore silk is famous for sarees. In India, 90% of the mulberry silk is produced in Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Assam.